- سبدخرید خالی است.
- ادامه خرید
Different Consensus Mechanisms: PoW Vs. PoS
The Rise of Cryptocurrencies: Understanding the Two Main Consensus Mechanisms
The world of cryptocurrency has exploded in recent years, with new coins and tokens being launched every day. As a result, there are several different consensus mechanisms that powers these digital currencies, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. In this article, we’ll delve into the two most popular consensus mechanisms: Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work is one of the earliest and most widely used consensus algorithms in cryptocurrency. It’s been around since the Bitcoin protocol was first released in 2009.
How it works
In PoW, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles, which involves:
- Hash function: Miners must find a hash that meets certain criteria.
- Block creation: The miner who finds a solution gets to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain and broadcast it to the network.
- Verification: Other nodes on the network verify the block by solving the puzzle themselves.
Benefits
PoW offers several benefits:
- Energy efficiency: PoW requires relatively low energy expenditure, making it more environmentally friendly than other consensus mechanisms.
- Security: The random nature of the puzzles makes it difficult for an attacker to predict the outcome and launch a 51% attack on the network.
- Speed: PoW blocks are generated and verified at a faster pace than PoS.
Drawbacks
PoW also has some drawbacks:
- Energy consumption: The energy required to mine cryptocurrency is significant, contributing to climate change and straining local power grids.
- Centralization: The need for powerful hardware and high computational resources can lead to centralization of mining operations.
- Vulnerabilities
: PoW makes it difficult to launch a 51% attack on the network due to the random nature of the puzzles.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake is an alternative consensus mechanism that’s gaining popularity in recent years. It was first introduced by Vitalik Buterin, the creator of Ethereum, and has since been adopted by other cryptocurrencies like Tezos and Cosmos.
How it works
In PoS, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on their stake in the network rather than having computational power. The process involves:
- Stake allocation: Validators are allocated a certain amount of cryptocurrency (stake) that they’re willing to hold for an extended period.
- Random selection
: A random list of validators is selected from the stake pool.
- Block creation: The randomly chosen validator creates a new block and broadcasts it to the network.
Benefits
PoS offers several benefits:
- Energy efficiency: PoS requires relatively low energy expenditure, making it more environmentally friendly than PoW.
- Security: The random nature of the selection process makes it difficult for an attacker to predict the outcome and launch a 51% attack on the network.
- Slower pace: PoS generates blocks at a slower pace than PoW.
Drawbacks
PoS also has some drawbacks:
- Centralization: The need for validators with significant stake can lead to centralization of the network, as more powerful individuals may accumulate more stake and influence.
- Scalability issues: PoS is still in its early stages, which can make it less scalable than PoW.
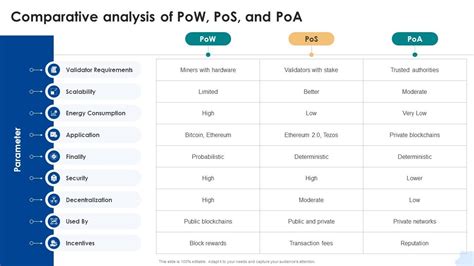
Comparison
| Consensus Mechanism | Energy Consumption (kWh) | Block Generation Time (seconds) |
| — | — | — |
| PoW | Low to moderate | Fast (10-30 seconds) |
| PoS | Moderate (2-5 kWh/million) | Slow (1-3 minutes) |
Conclusion
The choice between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake ultimately depends on the specific needs and goals of your cryptocurrency project.
