- سبدخرید خالی است.
- ادامه خرید
Ethereum: Bitcoin Mining: Block Structure
Here is an article on Ethereum’s block structure:
Understanding Ethereum: Block Structure
As a Bitcoin miner, it is important to understand how the blockchain works at the highest level. The Ethereum network uses a similar block structure, but with some key differences. In this article, we will explore Ethereum’s block structure and why it is important for miners.
What is a Block?
A block is a collection of transactions that are verified by nodes on the Ethereum network and added to the blockchain. It is essentially a digital container that holds a series of transactions that can include data, smart contracts, and more. Each block has a unique hash that serves as its fingerprint.
Ethereum Block Structure
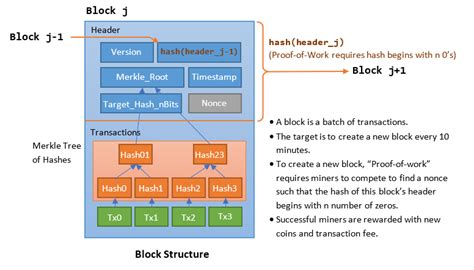
A standard Ethereum block consists of the following components:
- Header: The header contains metadata about the block, such as its number, timestamp, and the hash of the previous block.
- VChains: A variable-length list of VChan (VarChain) transactions, which are essentially packets of data with certain properties.
- RChains: A variable-length list of RChain transactions that contain more complex smart contracts or data structures.
- Locks: A set of locks, also known as a “lockstep,” that ensures the integrity and ordering of transactions within a block.
- Body: The actual VChan and RChan transactions.
Why is Ethereum’s block structure important?
Ethereum’s block structure has several implications for miners:
- Transaction verification: Each block must contain a set of verified transactions, which requires significant computational resources. Miners must solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate these transactions.
- Consensus mechanisms: The block structure is used as a consensus mechanism to validate blocks and ensure the integrity of the blockchain. Miners compete to validate blocks first, which can lead to a race condition.
- Block size limits: The Ethereum block size limit (1 MB) means miners have limited space to store and process transactions in each block.
Mining in Ethereum
As a miner, you need to understand Ethereum’s block structure in order to:
- Minimize energy consumption: Miners aim to solve complex mathematical puzzles quickly, which requires significant computing power. By understanding the block structure, they can optimize their energy consumption.
- Improve block time: Optimizing block time is crucial for miners to receive a reasonable reward per transaction. A well-structured block structure can help achieve this goal.
In conclusion, Ethereum’s block structure plays a crucial role in the functioning of the network. Miners need to understand and work within these limitations to successfully mine Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
